In our nearly eight years in the pumping industry, our technicians and engineers have found more than 80% of the problems with pumps come from the suction side.
Cornell Pump’s Installation and Care Guide outlines the key dos and don’ts of suction piping. Here are some highlights:
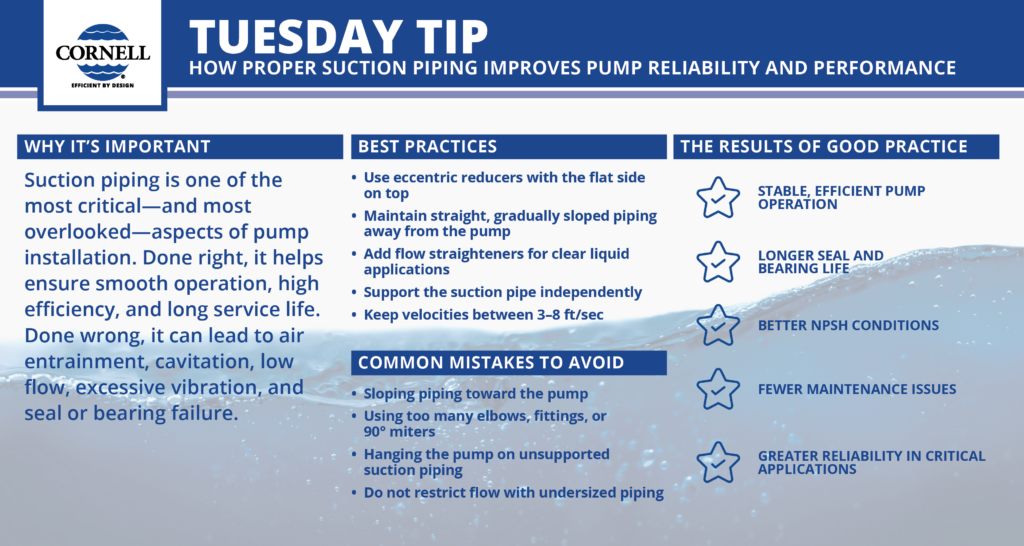
𝗕𝗘𝗦𝗧 𝗣𝗥𝗔𝗖𝗧𝗜𝗖𝗘𝗦 𝗙𝗢𝗥 𝗦𝗨𝗖𝗧𝗜𝗢𝗡 𝗣𝗜𝗣𝗜𝗡𝗚
- Use eccentric reducers with the flat side on top
This avoids trapping air at the reducer. Concentric reducers can hold air and lead to cavitation. - Maintain straight, gradually sloped piping away from the pump
Suction lines should slope slightly downward to the pump. Horizontal pipe runs should be straight for at least four pipe diameters before entering the pump. - Add flow straighteners for clear liquid applications
These devices help eliminate turbulence and uneven velocity distribution that can disrupt pump performance. - Support the suction pipe independently
Do not hang the pump from the pipe. Unsupported pipe adds stress that leads to bearing misalignment, vibration, and early mechanical seal failure. - Keep velocities between 3–8 ft/sec
This is general rule. This speed reduces friction losses and prevents vortexing at the inlet, but if you need to have a higher flow rate to reduce settling, you should use the increased flow –a plugged impeller is one of the worst suction side problems.
𝗖𝗢𝗠𝗠𝗢𝗡 𝗠𝗜𝗦𝗧𝗔𝗞𝗘𝗦 𝗧𝗢 𝗔𝗩𝗢𝗜𝗗
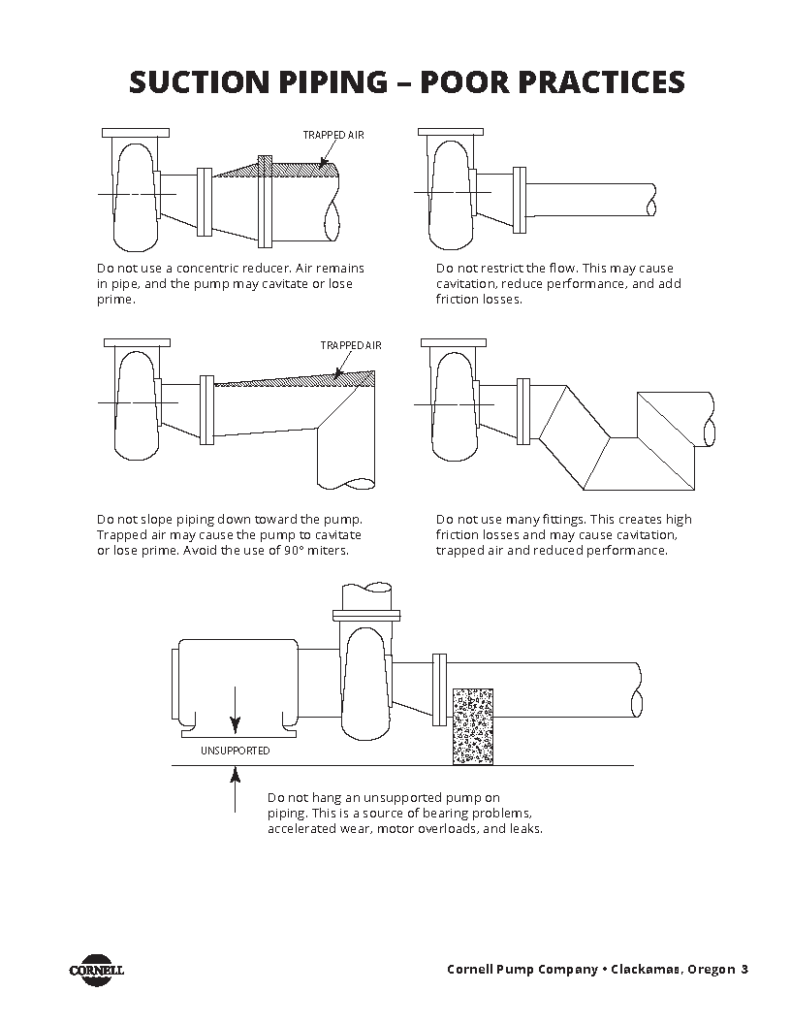
- Sloping piping toward the pump
This traps air, causing the pump to lose prime or cavitate. - Using too many elbows, fittings, or 90° miters
Sharp bends and unnecessary fittings increase friction loss and create turbulent flow. - Hanging the pump on unsupported suction piping
This leads to premature wear, leaks, and possible motor overload. - Do not restrict flow with undersized piping
Sudden changes in pipe diameter increase entrance losses and reduce NPSHa (Net Positive Suction Head Available).
𝗧𝗛𝗘 𝗥𝗘𝗦𝗨𝗟𝗧𝗦 𝗢𝗙 𝗚𝗢𝗢𝗗 𝗣𝗥𝗔𝗖𝗧𝗜𝗖𝗘
Good suction piping layout supports:
- Stable, efficient pump operation
• Longer seal and bearing life
• Better NPSH conditions
• Fewer maintenance issues
• Greater reliability in critical applications
Here are examples of poor piping from Installation and Care Guide