Why Redundancy Matters
- Operational Continuity
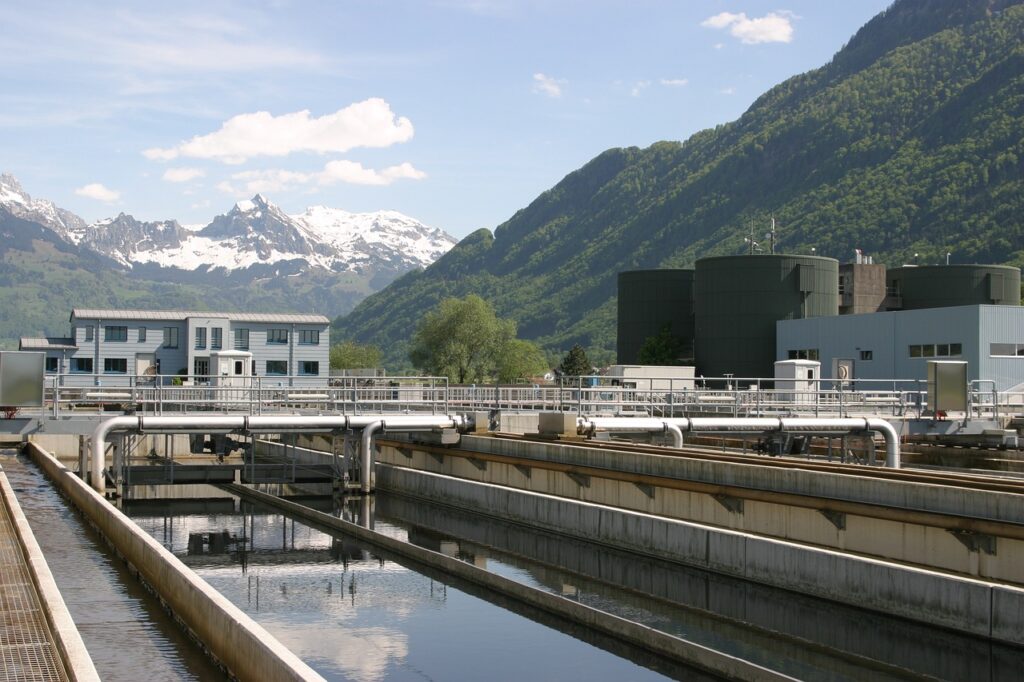
Pump stations are critical infrastructure. Redundancy ensures that if a primary pump fails, a backup is ready to maintain operation, preventing service disruptions or overflows. - Emergency Preparedness
Weather events, power outages, and mechanical failures are inevitable. Redundant systems allow municipalities to respond quickly, reducing the risk of costly environmental and property damage. - Maintenance Flexibility
With redundant pumps in place, routine maintenance can be performed without taking the entire system offline. This keeps operations running smoothly and minimizes downtime. - Regulatory Compliance
Many jurisdictions require redundancy in critical systems to meet environmental and safety regulations. Failing to provide it can result in fines, penalties, or forced shutdowns.
Common Redundancy Strategies
- Standby Pumps
Installing a standby (backup) pump that can automatically engage if the lead pump fails. - Lead-Lag Configurations
Systems designed to alternate between lead and lag pumps help balance wear and extend equipment life. - Parallel Pumping Systems
Multiple pumps operating together can adjust capacity as demand increases—offering both redundancy and scalability.
Cornell’s Commitment to Reliability
At Cornell, we engineer pumps designed for durability and efficiency—built to perform in mission-critical municipal applications. Our range of municipal pumps supports redundancy configurations, with features like dry-run capability, robust construction, and advanced monitoring options.
Redundancy isn’t just good practice; it’s a smart investment in long-term reliability and community service.
Learn more about Cornell’s municipal pump offerings at https://www.cornellpump.com/markets/municipal/ .
#MunicipalWastewater #SolidsHandling #PumpTechnology #Redundancy #CornellPump #Cycloseal #WastewaterSolutions #EfficientByDesign